At the core of every electric vehicle is a large, rechargeable battery pack that stores the energy required to propel the car. Just like petrol cars rely on petrol stations, EVs use charging stations to recharge their batteries. These stations can be installed at home or found in public places, making charging as convenient as filling up a tank of fuel.
Efficiency: EVs vs. Petrol Cars
One of the greatest advantages of electric cars is their superior efficiency compared to petrol vehicles. EVs convert 60% to 80% of the energy stored in the battery to power the wheels, while petrol cars convert only 17% to 21% of the energy stored in fuel into motion—the rest is wasted as heat. This stark difference means that EVs use energy much more efficiently, delivering more driving range for less energy.
How Electric Cars Move
Driving an electric car is remarkably straightforward. When you press the accelerator pedal, electricity from the battery flows to the motor, which spins and turns the car’s wheels. The response is immediate, providing instant torque for quick acceleration and smooth driving without the lag associated with traditional engines.
Range anxiety is a common concern, but it’s less of an issue than most think. Most EVs can travel up to 250 miles on a single charge, more than enough for daily commuting and errands. Long-range models like the Tesla Model S can go even further, reaching 450 miles on a single charge. For context, the average daily commute in Nigeria is about 30 miles, well within the range of most electric vehicles.
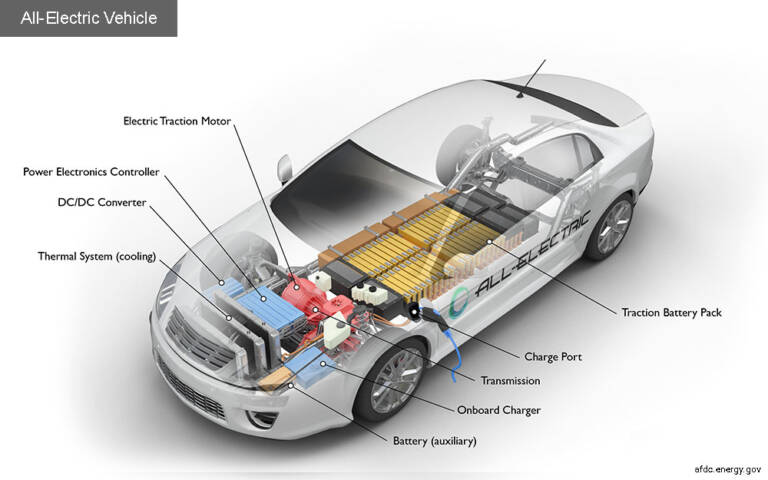
Key components of an electric car:
- Battery:The main source of power for the motor. It stores the electricity needed to move the car.
- Charging port: This is where you plug in your EV to recharge the battery, either at home or at a public station.
- DC/DC converter: Converts high-voltage DC power from the battery into low-voltage power to run other vehicle systems (lights, wipers, etc.).
- Electric traction motor: This component converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to power the wheels.
- Thermal management system: Keeps the vehicle and its components (especially the battery) at optimal operating temperatures to maximize performance and lifespan.
- Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
- Power electronics controller: Manages the flow of electricity to control speed, torque, and efficiency.
- Onboard charger: Converts the electricity coming from the charging port into DC power to charge the battery.
- Transmission: Transmits power from the electric traction motor to the wheels to enable the car move.
But that’s not all. Electric cars also gives you a quiet and peaceful driving experience, accelerating quickly and smoothly, without the jarring vibrations of traditional petrol cars.
Plus, they are better for the environment, produce zero emissions, and help combat climate change.
Not to mention cost savings. A recent study shows that the average EV owner will spend 80% less to power the car and 50% less to maintain it when compared to the average petrol car owner. No oil changes or frequent servicing needed!
Ready to make the switch to EVs? Join the electric revolution and experience the future of transport today


